Quick Navigation
Ubuntu 22.04 with MySQL
This comprehensive guide covers all steps to launch and verify your MySQL instance on Ubuntu Server 22.04.
Overview: This AMI provides a pre-configured Ubuntu 22.04 LTS environment with MySQL, ready for immediate database operations. Built on the latest Ubuntu LTS release, this AMI combines the performance enhancements of Ubuntu 22.04 with MySQL’s robust features to handle a wide range of data workloads.
Step 1: Launch EC2 Instance
- Navigate to the MySQL on Ubuntu 22 AMI
- Click “Continue to Subscribe”
- Accept the terms and click “Continue to Configuration”
- Select your preferred AWS region
- Click “Continue to Launch”
Recommended Configuration
- Instance Type: t3.medium or higher
- Storage: Minimum 20 GiB (50 GiB recommended for production)
- Security Group:
- Port 22 (SSH)
- Port 3306 (MySQL) – Only open to trusted IPs
Step 2: Connect to Your Instance
Secure Shell (SSH)
- Wait for the instance to reach the running state in your cloud console
- Locate the instance’s Public IP address
- Use an SSH client (like Terminal on macOS/Linux, or PuTTY/Windows Terminal on Windows) and your private key file
- The default username for Ubuntu AMIs is typically ubuntu
ssh -i /path/to/your-key-pair.pem ubuntu@<Instance-Public-IP>
Username: ubuntu
Key File: /path/to/your-key-pair.pem
Instance IP: Your instance public IP
Step 3: Verify SQL Server Installation
Once connected to your Ubuntu Server, verify the MySQL service is active and operational using these methods:
Method 1: Check Package Installation Status
systemd under the service name mssql-server.
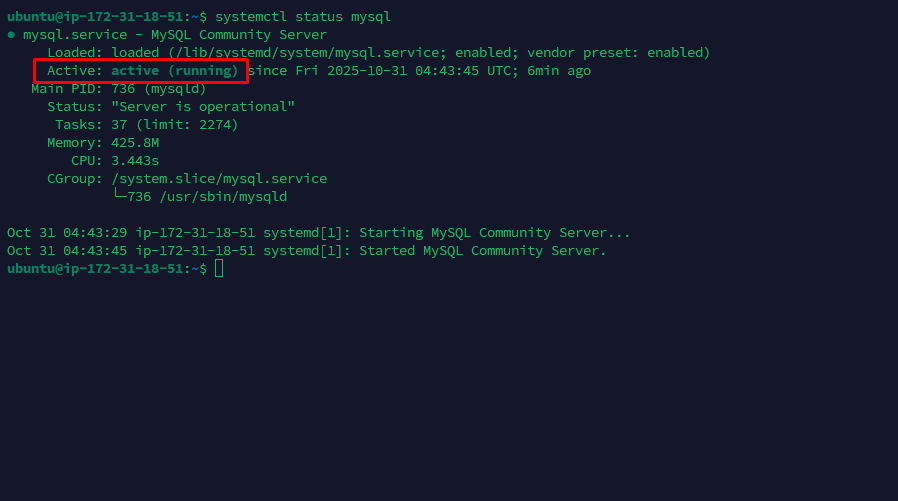
- Run the following command in your SSH terminal:
systemctl status mysql- Verification: The output should show the service status as active (running)
Method 2: Check Package Installation Status
mysql-server package is installed on the system using the Debian Package Manager (dpkg).
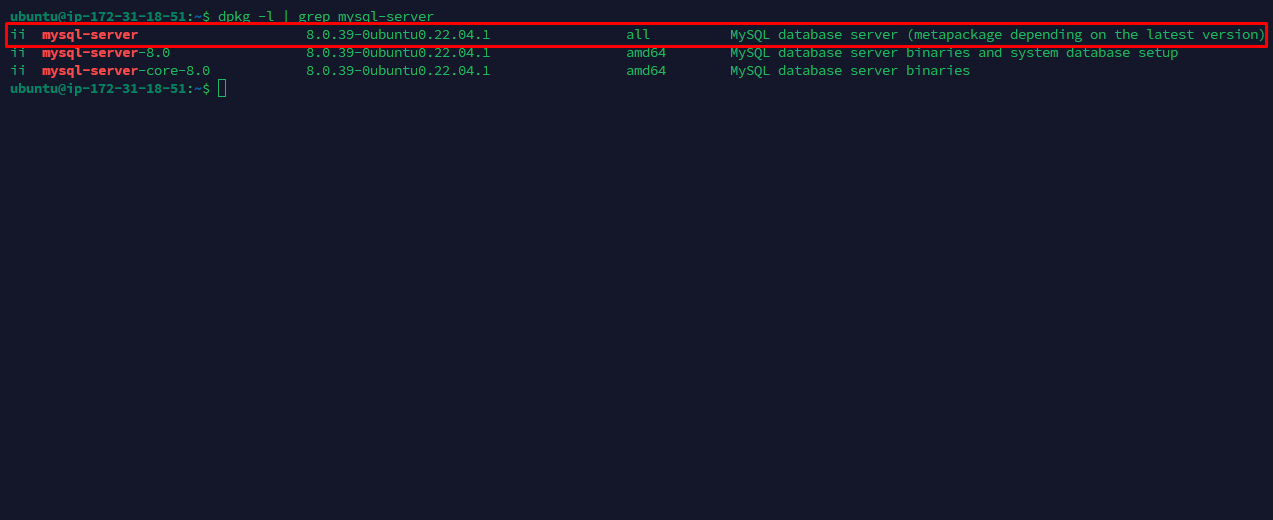
- Run the command:
dpkg -l | grep mysql-server- Verification: The output should start with
ii mysql-server, which indicates the package is installed (i) and configured (i).
Expected output:
ii mysql-server 8.0.x-0ubuntu0.22.04.x all MySQL database server
ii= Installed and configured confirms the MySQL Server package is properly installed.
Method 3: Check MySQL Version
- Run the command:
sudo mysql --version- Note: No password is set for the root user by default.
- Verification: The output should return the MySQL version information.
Expected output:
mysql Ver 8.0.x-0ubuntu0.22.04.x for Linux on x86_64 ((Ubuntu))
- Successful version output = MySQL client is properly installed and accessible.

Related SQL Server AMIs
SQL Server 2019 Standard on Ubuntu 20.04
Run SQL Server 2019 on Linux with Ubuntu Server for cost-effective and flexible database hosting.
SQL Server 2019 Standard on Windows 2019
Standard edition with essential database features for mid-sized workloads, reliable performance, and basic high-availability support.
SQL Server 2019 Enterprise on Windows 2019
Enterprise edition with advanced features for mission-critical workloads and large-scale deployments.
Browse All AMIs
Browse our entire AMI catalog, offering a full spectrum of OS, application, and infrastructure solutions.
